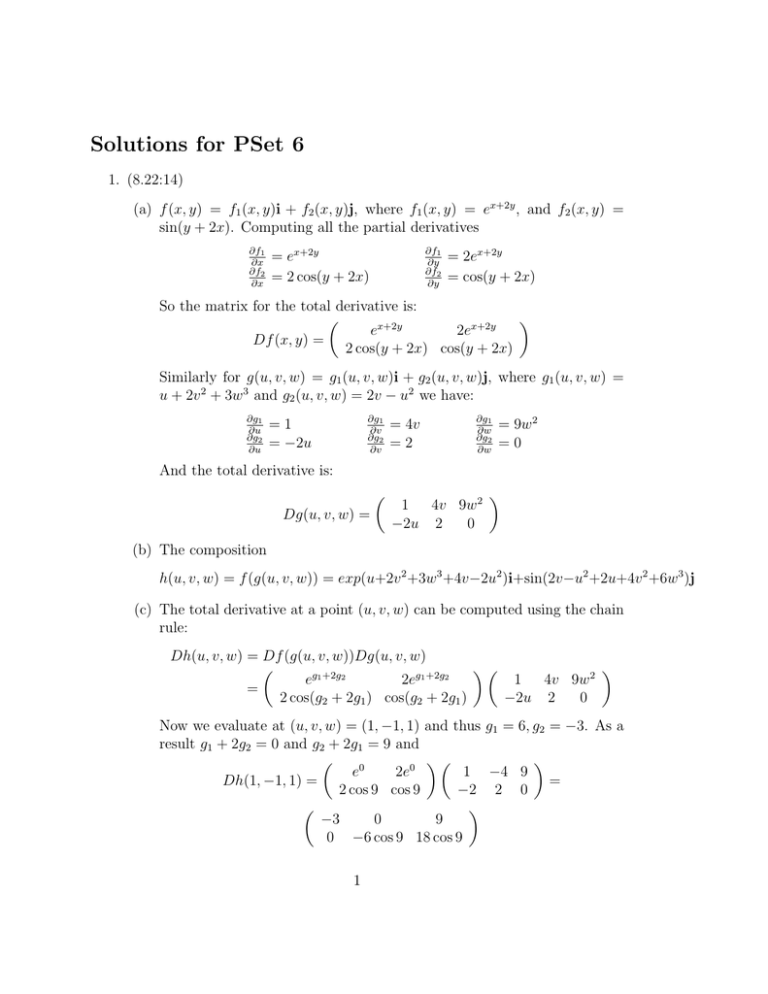
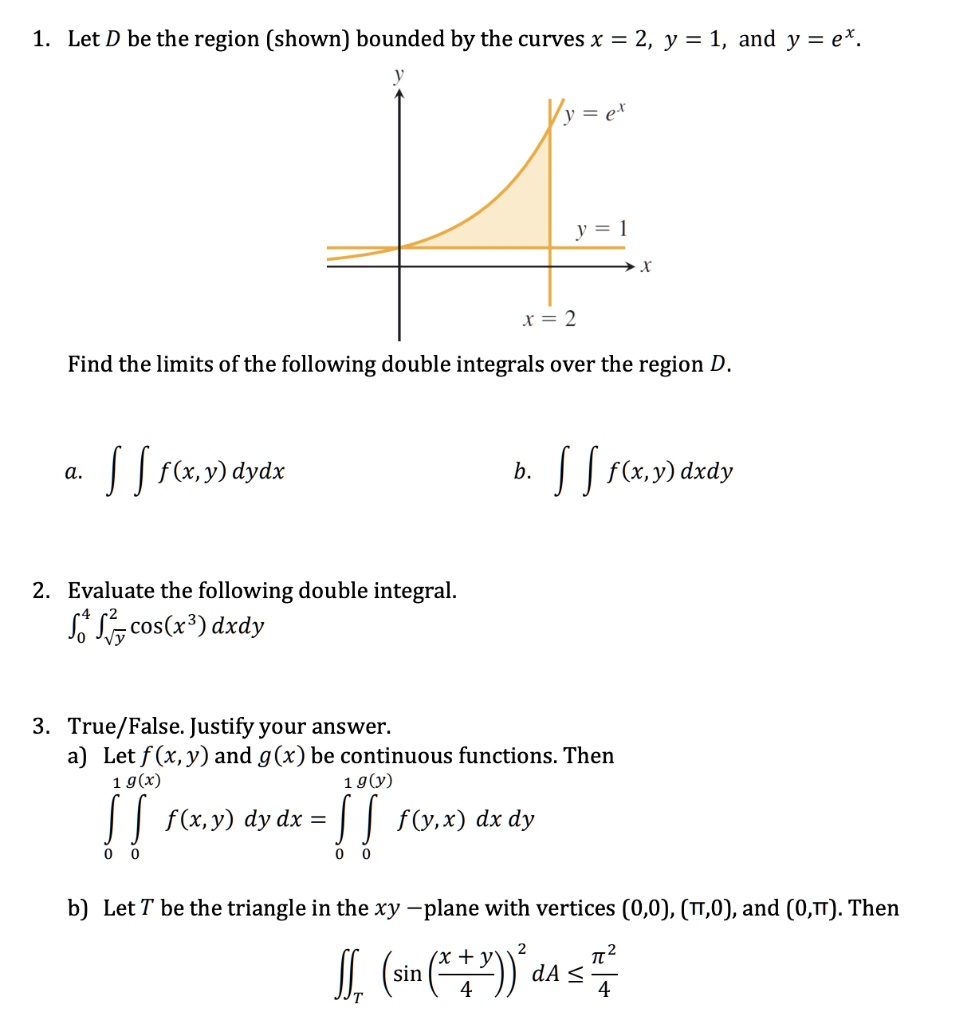
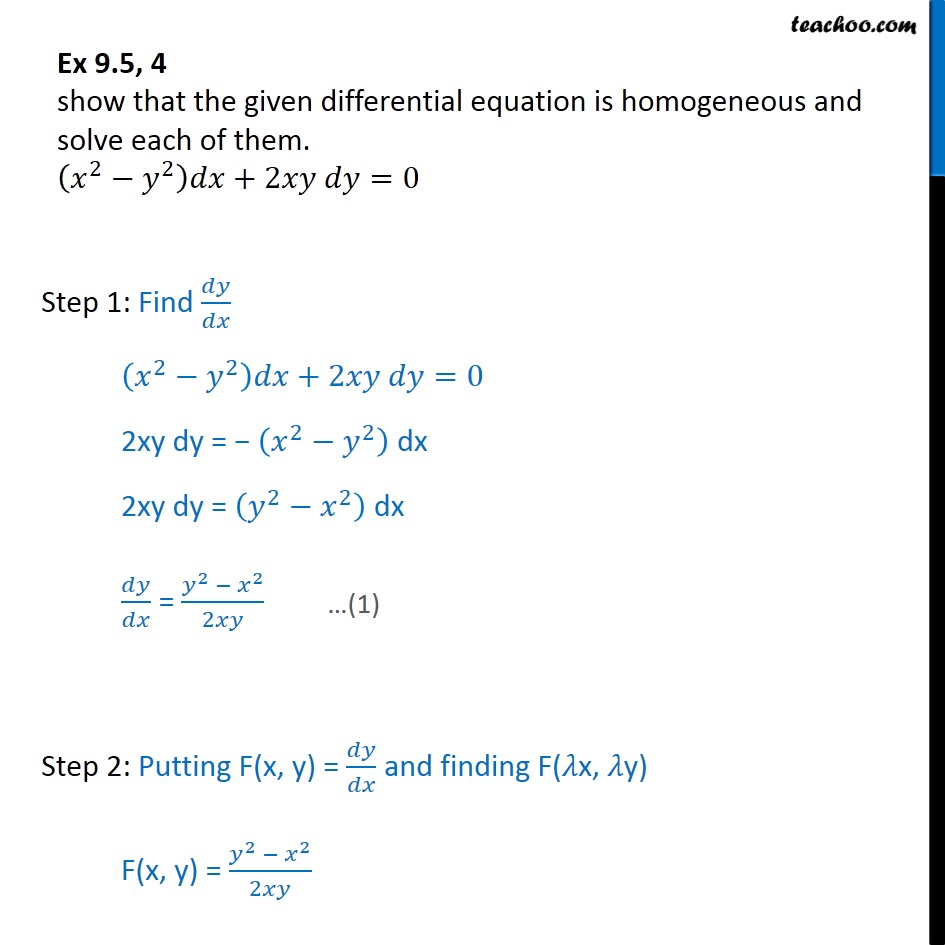
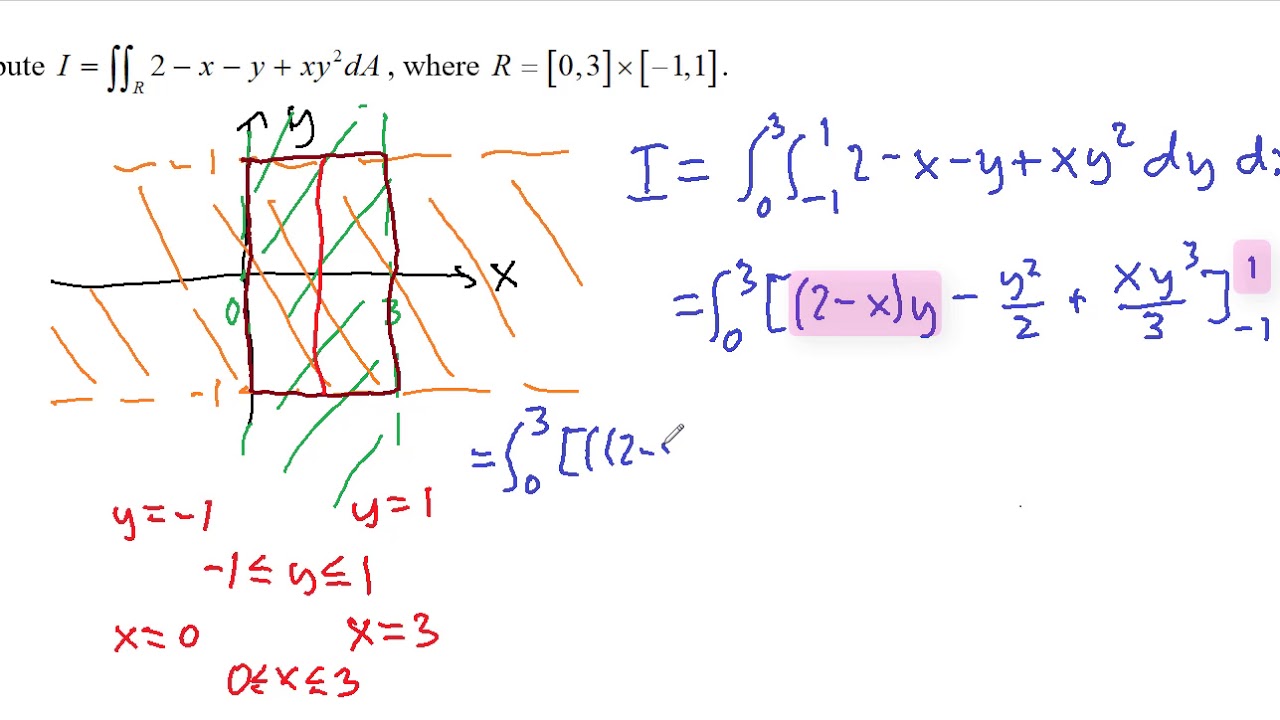
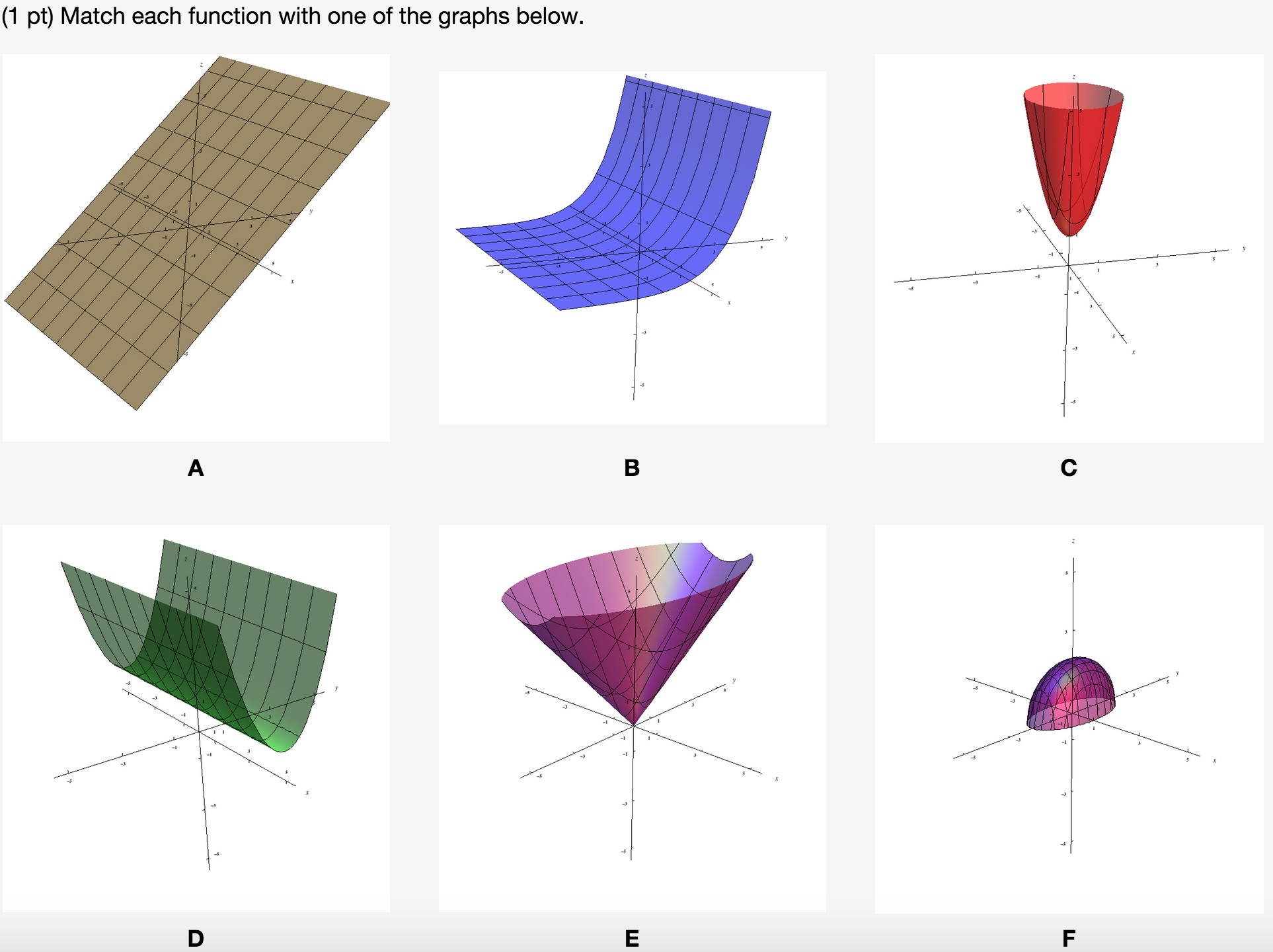
Calculus questions and answers Find the absolute extrema for f (x, y) = e^−x^2−y^2 (x^2 2y^2 ) over the closed disk D x^2 y^2 ≤ 4
F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph-Piece of cake Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math InputDirectrix y = −1 4 y = 1 4 Select a few x x values, and plug them into the equation to find the corresponding y y values The x x values should be selected around the vertex Tap for more steps Replace the variable x x with − 1 1 in the expression f ( − 1) = ( − 1) 2 f ( 1) = ( 1) 2 Simplify the result
F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graphのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 | ||
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
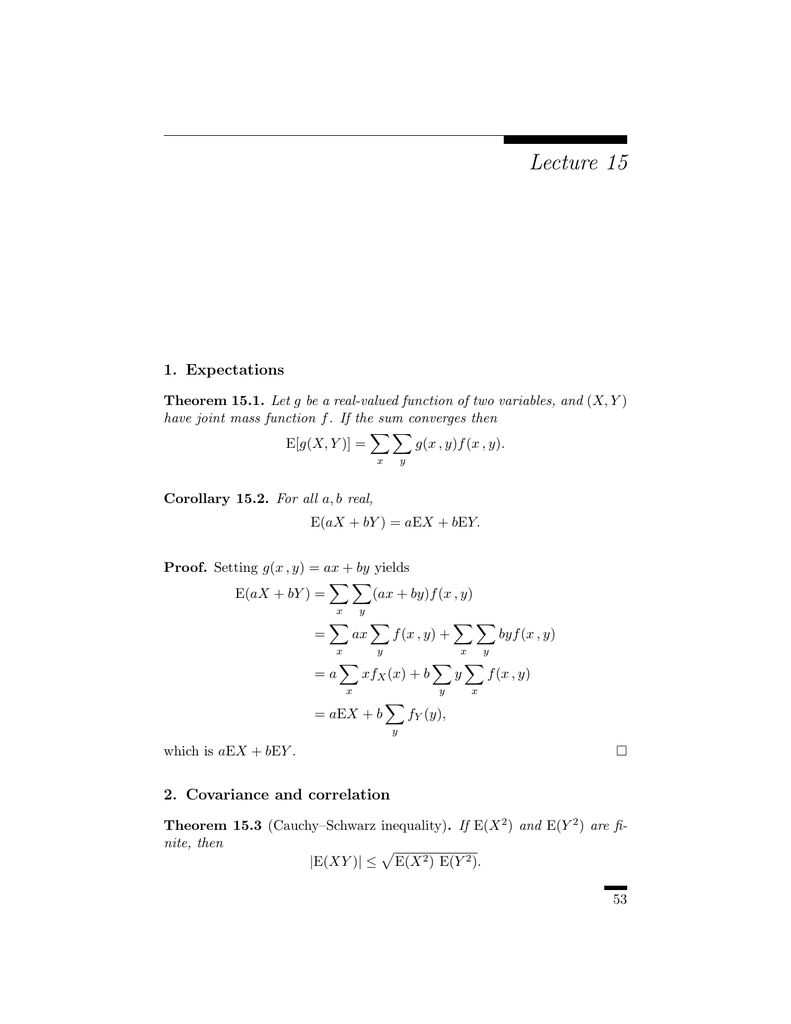 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | 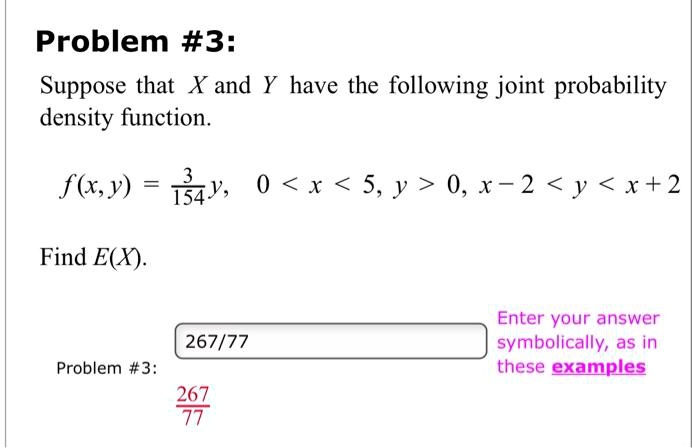 |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
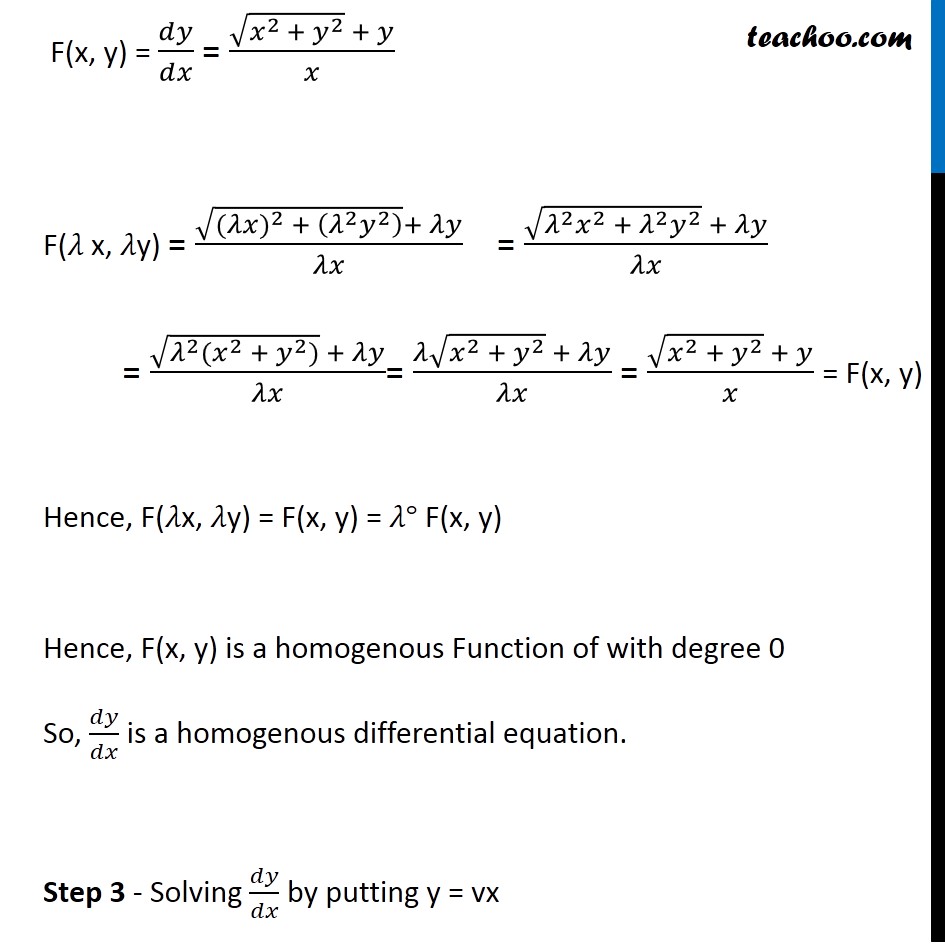 |  | |
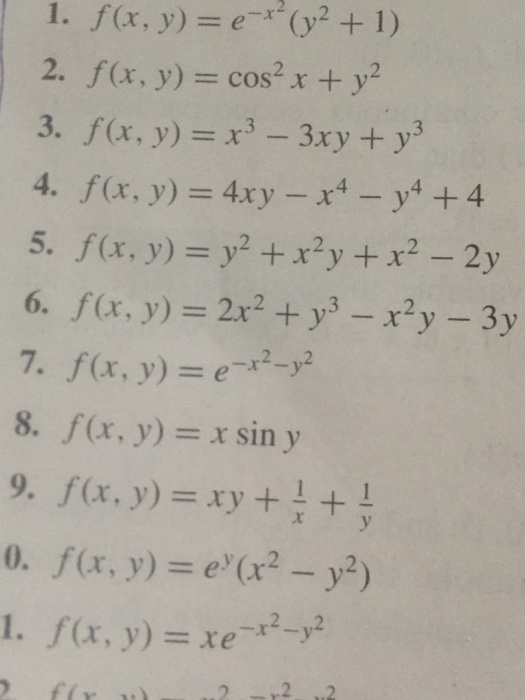 |  | |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
 | ||
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
「F(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |
Get the free "Surface plot of f(x, y)" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle Find more Engineering widgets in WolframAlphaDivide f2, the coefficient of the x term, by 2 to get \frac{f}{2}1 Then add the square of \frac{f}{2}1 to both sides of the equation This step makes the left hand side of the equation a perfect square
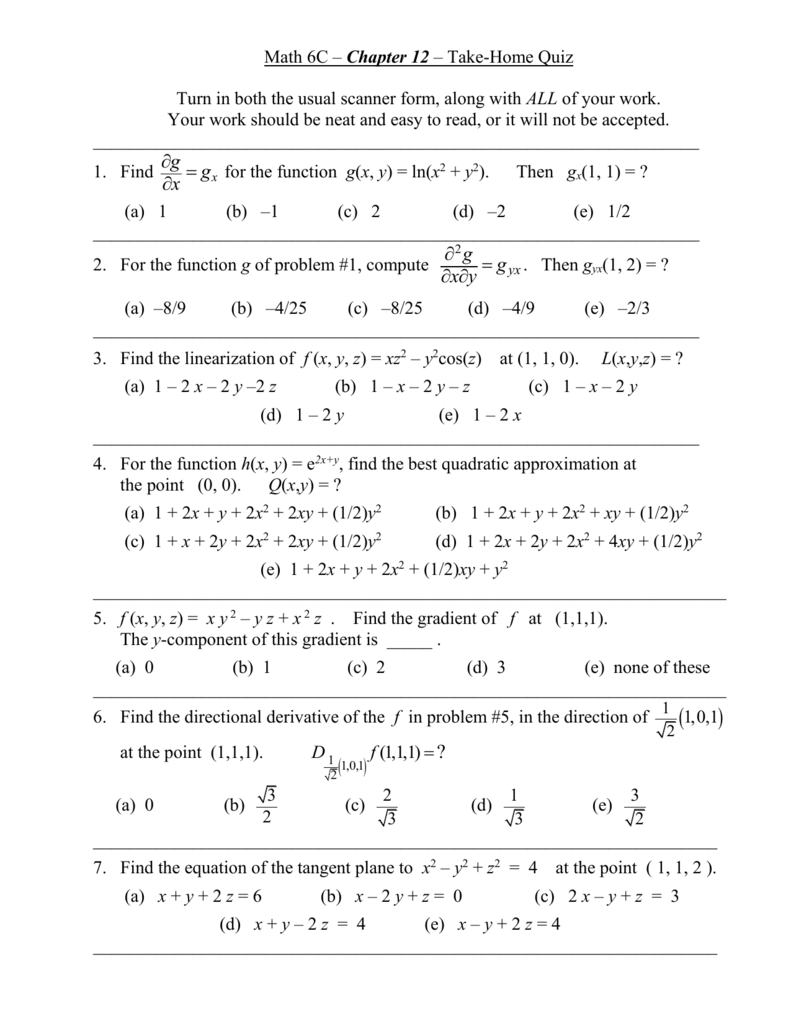
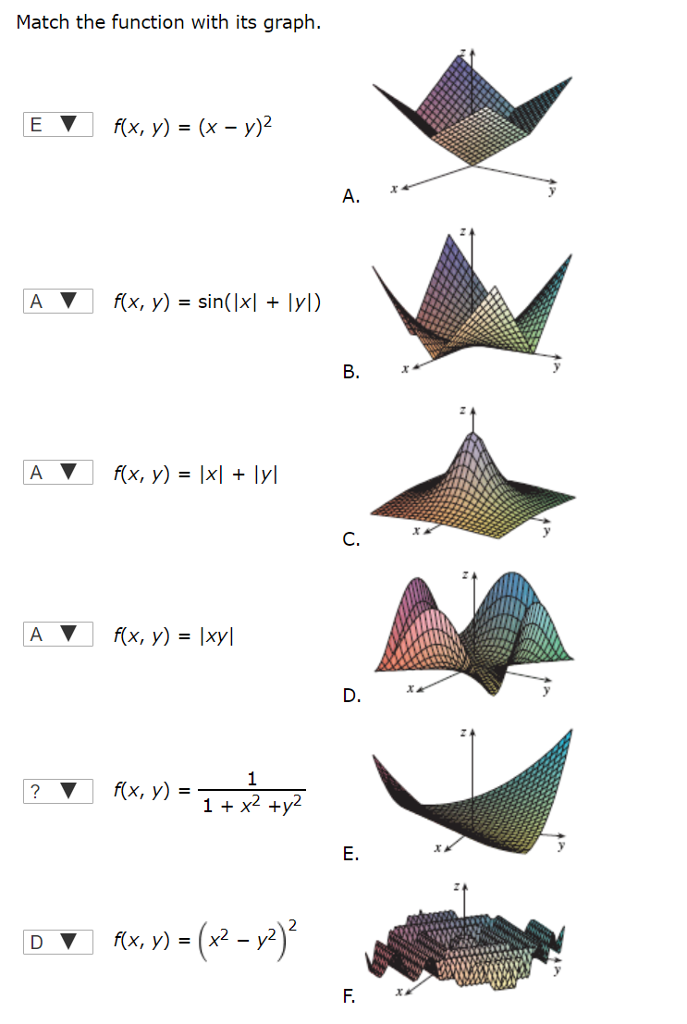
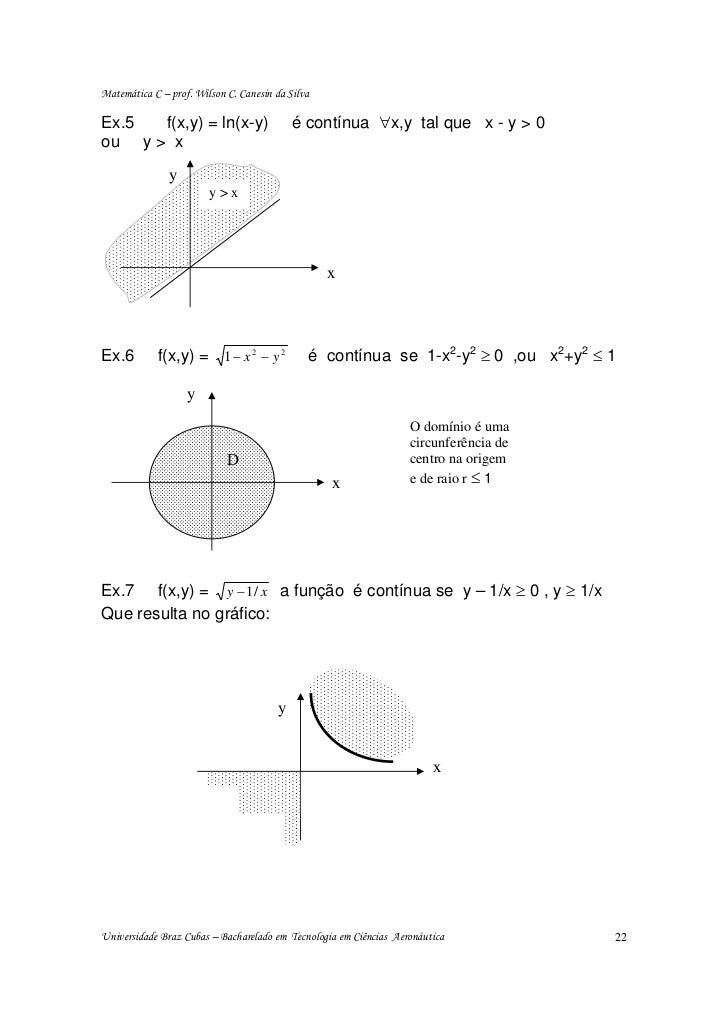
Incoming Term: f(x y)=e^-(x^2+y^2), f(x y)=4-x^2-y^2, f(x y)=3-x^2-y^2 graph, f(x y)=e^(4y-x^2-y^2), f(x y)=sqrt(4-x^2-y^2), domain of f(x y)=e^-(x^2+y^2), f(x y)=sqrt(4-4x^2-y^2), f(x y)=x^4-2x^2+y^3-3y, f(x y)=(x^3y-xy^3)/(x^2+y^2), f(x y)=x^2+y^4+2xy,



